The invention herein disclosed relates to a new cationic steroid showing antibacterial, antifungal, and antibiofilm activities, including when immobilized in coating polymers.
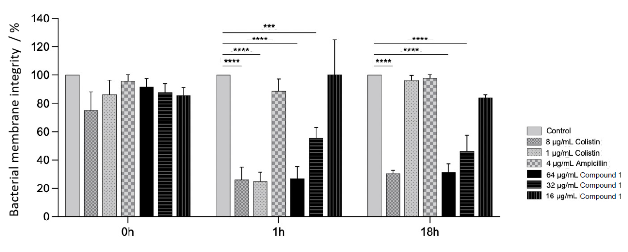
The present invention provides an amphiphilic small-molecule with bactericidal and fungicidal activity. The compound is synthetized in scalable conditions from readily available and cheap building blocks. The molecule shows significant biocidal activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria, including the ESKAPE pathogens, and fungi. Notably, the compound acts synergistically with amphotericin B and fluconazole against the reference Candida albicans strain. Significant dose-dependent disruption of bacterial membranes is observed upon treatment with the new cationic steroid. Polymeric coatings containing up to 1.5 % w/v cationic steroid sustain effective reduction of the formation of Escherichia coli biofilms in ureteral stents, in relevant hydrodynamic conditions.
One-step scalable synthesis starting from low-cost commercial building blocks; Antibacterial and antifungal activity with minimal inhibitory concentrations between 16 and 128 µg/mL; Retains antibiofilm activity when incorporated in polymeric coatings.
Antimicrobial therapeutics against veterinary and/or human pathogens; Antimicrobial coating or disinfection of medical devices; Mild detergent for emulsification of lipids; Aquaculture feed formulations for infectious disease control.






